Pricing of services in an electricity transmission network raises the same issues as in regulated communications industries
During Analysys Mason’s 30-year history we have supported communications regulatory authorities on costing and tariffing of upstream and downstream components of end-user services, in the context of evolving legislative priorities, regulatory policies and market dynamics. There has been constant advancement in the communications industry, leading to changes in the solutions to these regulatory problems.
Most of our work has been in the electronic communications and broadcast media industries, with more recent work extending into the postal sector. But in 2014, Analysys Mason provided expert support on the level of network usage tariffs in the electricity industry, as part of a project for a regulatory client, working with energy sector experts Economic Consulting Associates. Our extensive history of involvement in network industry policy and regulation, knowledge of infrastructure cost and revenue drivers, as well as our detailed understanding of the mechanics of costing and pricing allowed us to contribute an external perspective to the issues in this study. In particular, the regulator wanted to understand why some end-user tariffs charged by electricity suppliers were high – indeed, among the highest in Europe. Underlying this was a concern about the attractiveness of the country to businesses and enterprises.
Our project concluded that the allocation of costs between customer categories was causing some tariffs to be relatively high. We also concluded that the level of non-network mark-ups (associated with support, collection and a public service levy) contributed to higher prices. Our conclusions were based on a combination of:
- cost benchmarking, using a transformation of comparable costs and mark-ups from other jurisdictions. Here, it was not straightforward to map tariffs across countries, because the different cost components and levies had to be separated and re-combined to obtain a like-for-like comparison
- tariff design modelling which simulated the cost recovery (revenue) requirements across a basket of user types. This involved calculating costs for different assumed user profiles and tariff plans.
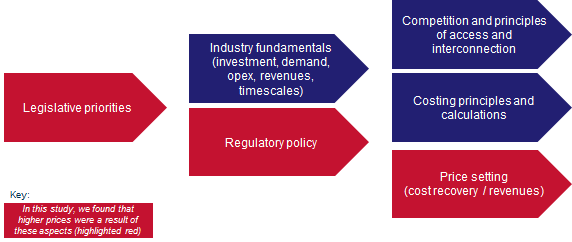
Our conclusions on higher prices touch on a number of aspects of price setting in regulated industries, as illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Price setting in regulated industries [Source: Analysys Mason, 2014]
Different network industries share many characteristics – as well as the experience, tools and techniques used for regulatory and policy investigations. The main areas of similarity are highlighted in Figure 2. Where the industries do differ, this leads to different regulatory and policy approaches, often highly specific to the situation and needs of the consumer, industry and government stakeholders.
Figure 2: Similar issues encountered in regulated network industries [Source: Analysys Mason, 2015]
| Industry characteristics | Fixed telecoms | Broadcast media | Postal services | Electricity transmission |
| Politically motivated objectives (e.g. affordability, ubiquity, environmental concerns, efficiency) | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Utility with (near) uniform tariffs for multiple products and services (which are broadly similar) | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Extensive access/delivery network | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Dedicated lines per customer, very high capacity per access line | Y | Only IPTV | Y | |
| Shared network for different types of "traffic" (e.g. off-peak, guaranteed bandwidth, high capacity) | Y | Y | Y | |
| Large, mainly fixed cost of network infrastructure | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Multiple players in the end-user value chain | Y | Y | Sometimes (e.g. business mail) | Y |
| Non-linear relationship between units carried and incremental cost | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Demand and supply forecast uncertainties | Y | Y | Y |
Our recent work in the electricity transmission industry builds on our similar understanding of communications and electronic transmission networks. This demonstrates our skills and flexibility in fitting our advice to the specific needs of individual markets and regulatory authorities, whatever the sector.
Analysys Mason can provide advice on a wide range of issues, from policy formulation to regulatory implementation and stakeholder monitoring of regulated network industries. We have been actively supporting our clients on these issues in evolving, dominated or competitive markets since the liberalisation of telecoms monopolies began, around 30 years ago. Some of the topics we have covered include: investment planning, regulatory accounting, scarce resource allocation, efficiency, cost modelling, pricing, quality-of-service monitoring, upstream input requirements, technology studies, competition policy, wholesale conditions, significant market power remedies and consumer issues.
Authors


