Considerations on set-asides and coverage obligations in 5G mid-band auctions
Analysys Mason worked on a study during January 2022 with the Canadian telecoms company, TELUS, to examine pro-competitive measures and coverage obligations for 5G spectrum in the 3400–4200MHz mid-band in various countries. The study was motivated by a consultation by the Canadian government on a policy and licensing framework for spectrum in the 3800MHz band, which sought input on various questions including network build-out requirements.
As part of its response to the Canadian government’s consultation, TELUS asked Analysys Mason to compare how spectrum in the 3400–4200MHz band has been awarded in 24 high-income countries, all of which are members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Our report discusses that the focus of mobile network investment in the 5G era is on deploying new mid-band capacity with spectrum in the 3400–4200MHz band as a means of introducing new mobile services. National regulators can opt to make mid-band spectrum available in various ways and may seek to satisfy differing objectives through pro-competitive measures and coverage obligations.
The report compares the different measures that apply in the selected countries, including spectrum caps, coverage obligations and other options to incentivise coverage roll-out.
Some of our findings are as follows.
- Most OECD countries considered in the study implemented mid-band spectrum caps. 22 of the 24 countries in the benchmark set used (or initially planned to use) auctions to assign mid-band spectrum, and most of these (19 of the 22) applied spectrum caps in these auctions.
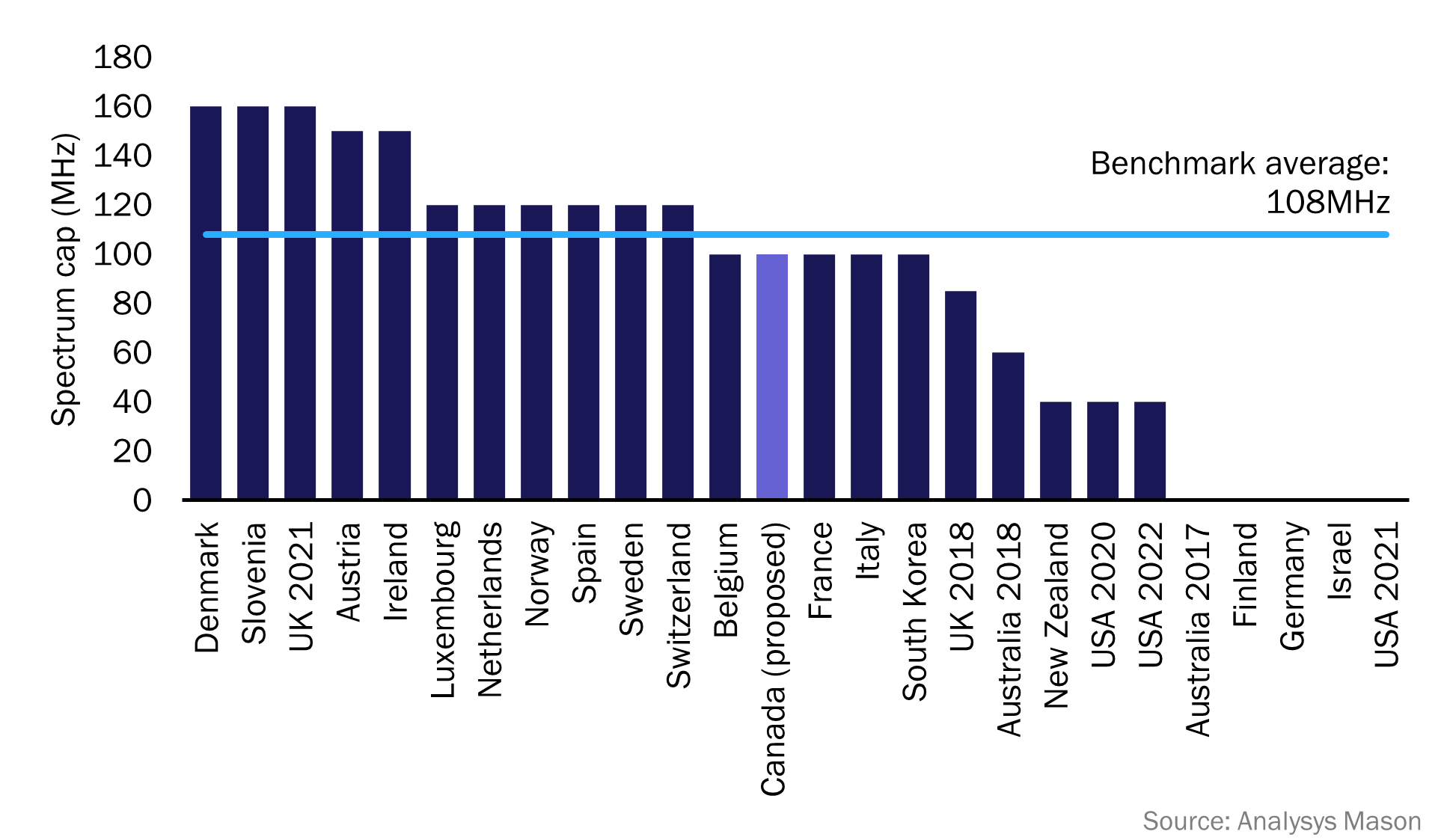
- Caps were set at an average level of 108MHz in the benchmark countries, and at least 100MHz per operator was permitted in most cases (Figure 1).
- There are only six benchmark countries (including Canada) where no operator holds 100MHz of mid-band spectrum.
- Coverage obligations or incentives are an important component of a spectrum auction for ensuring that spectrum is deployed extensively and in an efficient manner. This is especially true in countries with unique geographies, including significantly sized rural areas. Options for offering coverage incentives rather than just obligations may be relevant for rural areas.
Figure 1: Mid-band spectrum caps in the benchmark countries that used auctions
Our detailed findings can be found by reading the report, Pro-competitive measures and coverage obligations in mid-band auctions. For more information on this topic, please contact Janette Stewart, Partner.
Article (PDF)
DownloadAuthor
Janette Stewart
Partner, expert in spectrum policy, pricing and valuationRelated items
Article
New thinking on spectrum valuation is needed for upper mid-band frequencies
Article
Why spectrum renewal policy matters for network investment and service quality
Article
Does the mobile market need additional sub-1GHz spectrum?

