Enterprises will spend USD9 billion on private networks by 2028 but the market will not have reached its potential
The number of private LTE/5G networks worldwide will grow from over 4000 in 2022 to over 60 000 in 2028, according to Analysys Mason’s recent report Private LTE/5G networks: worldwide trends and forecasts 2023–2028.1 The forecast projects the number of private networks and associated capex and opex, split by region, sector and technology. Network spend will increase from USD1 billion in 2022 to USD9 billion in 2028 – a CAGR of 48% – but will be less than 5% of the equivalent spend on public network infrastructure in 2028.2
Interest in private networks remains high despite the relatively modest long-term opportunity. Private networks will provide a small boost to operators’ enterprise revenue while other segments struggle to grow, and can help operators to develop capabilities such as professional services and vertical-specific expertise. For established network vendors, it represents useful incremental revenue. For start-up vendors, even a market of just a few billion US dollars is hugely attractive. Operators and vendors are also using private 5G to demonstrate real-world examples of the technology because 5G activity on public networks remains limited.
Industrial sectors are leading the deployment of private networks
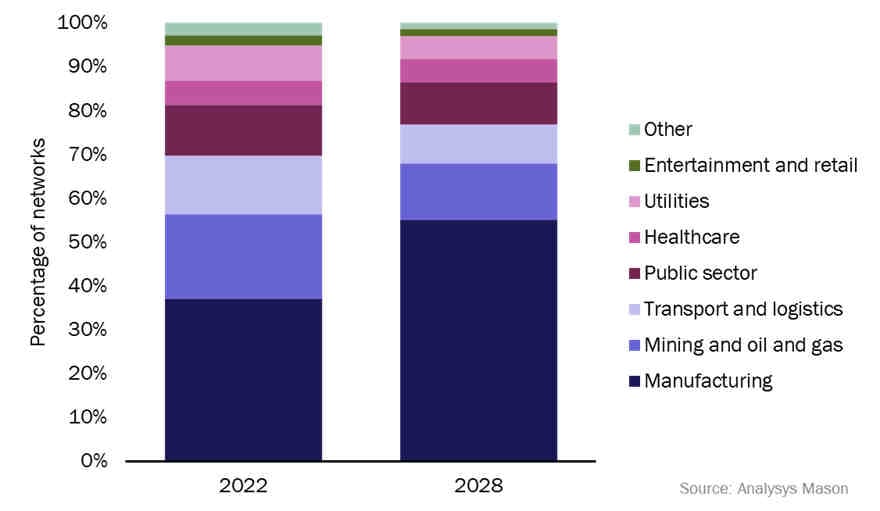
Private networks activity has been strong in industrial sectors such as manufacturing, transport and mining (Figure 1). The manufacturing sector in particular is driving the market.
Automation and cost savings are clear drivers for the use of private cellular and there are numerous small-sized factories worldwide (in contrast to sectors such as mining, which contain a small number of large sites). As such, we forecast the manufacturing sector will account for over half of all private networks deployed by 2028.
Figure 1: Share of private networks by sector, 2022 and 2028
Efficiency gains and flexibility over other technologies are key drivers to adoption; cost and complexity are hurdles
Total spend on private networks will reach USD9.2 billion by 2028. Key drivers of spend on private networks include the following.
- Operational efficiency. Large organisations’ digital transformation programmes are underway. Private networks are being used to support the process by digitising enterprises’ data and using it to create new digital products and services. Automating processes and the remote control of assets are frequently cited as the motivation for using private networks.
- Replacing legacy/fixed networks. Private wireless networks can support applications such as automated guided vehicles as a flexible and relatively cost-effective alternative to extending wired networks.
- Limitations of Wi-Fi. Private LTE/5G is rarely deployed to replace existing Wi-Fi networks completely. The two technologies will co-exist and private cellular will support applications where Wi-Fi performance is limited. This includes outdoor coverage of large sites, where Wi-Fi may not be cost-effective, and indoor sites such as factories, where dedicated spectrum can perform better than Wi-Fi in ‘noisy’ signal environments.
The private networks market also faces barriers that are holding back adoption.
- Cost. Private cellular can be expensive. Most deployments today are based on a dedicated, on-premises model that has both a capex and opex element, which can require significant up-front investment. Alternative opex-only pricing models are gradually emerging, which may be better suited to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Even so, private networks will still not be as cheap as Wi-Fi.
- Complexity. The market is currently highly bespoke and custom requirements create barriers to scale. Sector requirements are diverse; even within sectors, enterprise needs vary. This makes it difficult for suppliers to develop propositions that can be replicated across sectors.
- Devices. 5G devices are expensive and not widely available.
Some factors such as equipment cost and device availability will improve with time as the private networks ecosystem develops and suppliers gain economies of scale. Complexity is more difficult for private network players to tackle. Enterprises would ideally like private networks to be as simple to deploy and manage as Wi-Fi, but private cellular currently requires extensive network planning, systems integration and ongoing support.
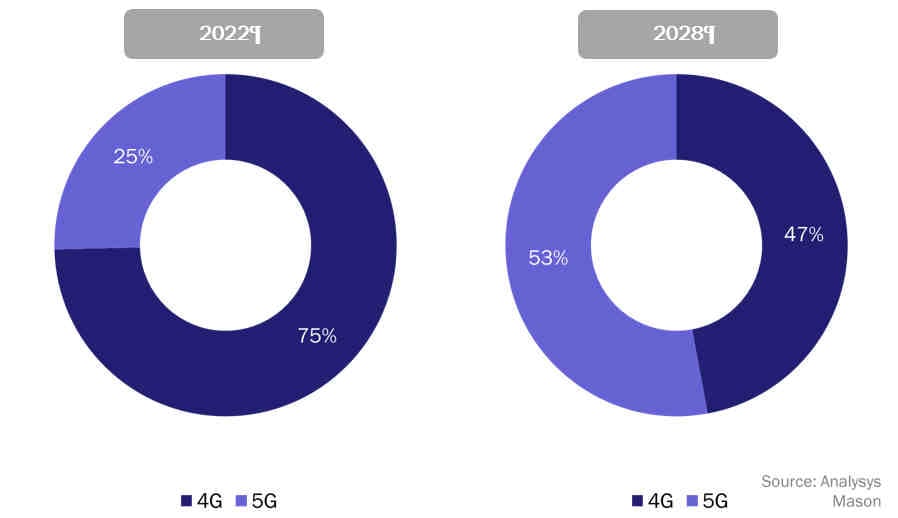
LTE was the dominant technology in 2022 but almost half of all private networks will be 5G networks by 2028
Projecting the technology split of private networks is challenging due to the prevalence of converged LTE-5G core networks. Several private networks are announced as 5G networks, but in practice, deploy a converged core which supports both LTE and 5G and have many more LTE than 5G devices on the network.
We estimate that 75% of private LTE/5G networks used LTE at the end of 2022 but this will fall to 53% by 2028. Interest in private 5G is high but limited device availability and costs have held back adoption. Many private 5G networks are at the trial stage. In contrast, private LTE has existed for over a decade and some early adopters have progressed from a single network to deployments across multiple sites.
Figure 2: Share of private networks by technology, 2022 and 2028
The size of the private networks opportunity in the long term depends on providers reducing costs and complexity
Private LTE/5G networks have mostly been deployed by large enterprises and organisations and we expect this trend to continue throughout the forecast period. The market will look considerably different when these opportunities slow down and private network providers then target smaller firms. Suppliers will need to adapt their propositions so that they are cheap and simple enough to be adopted by SMEs. Private network providers are gradually taking steps to achieve this, with flexible pricing options and using hybrid deployment models, for example, but it will take a few years to spread across the market.
1 Analysys Mason defines a private LTE/5G network as a cellular network that is built specifically for an individual enterprise, where at least one of the network elements (packet core or radio-access network) is deployed on-site. We do not include virtual private networks delivered over public infrastructure.
2 For more information see Telecoms capex: worldwide trends and forecasts 2018–2028.
Article (PDF)
DownloadAuthor

Ibraheem Kasujee
Senior AnalystRelated items
Article
Ericsson’s reorganisation of its enterprise wireless unit should help to streamline its private network offering
Forecast report
Private LTE/5G networks: worldwide trends and forecasts 2024–2029
Tracker
Private LTE/5G networks tracker 2Q 2024

