Economic impact of Google’s submarine cable network in Latin America and the Caribbean
15 May 2023 | Regulation and policy
David Abecassis | Tom Wicken | Andrea Betteto | Dr Michael Kende | Prof. Neil Gandal (independent adviser)
Report
In this report, sponsored by Google, Analysys Mason analyzed the impact of submarine cables in Latin America and the Caribbean region (LAC). We quantified the economic impact of cables landing in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Panama, and Uruguay in which Google has invested.
Like in the rest of the world, Internet services are vital for the LAC region. Services and products are growing rapidly, creating very substantial demand that needs to be met on an international basis. As part of this global trend, Internet traffic both within the LAC region and between LAC countries and the rest of the world is forecast to continue to grow in the future. It is in this context that operators and Internet companies, alongside some infrastructure investors, are investing in the LAC region in order to support the expected traffic growth.
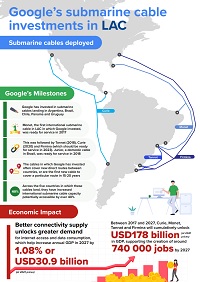
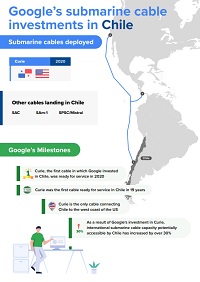
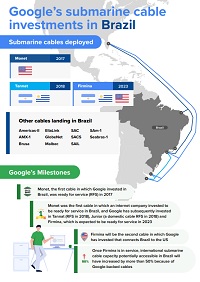
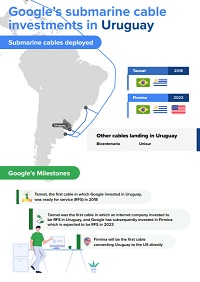
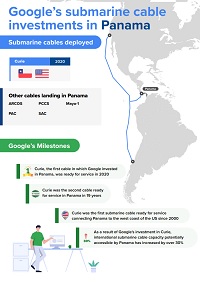
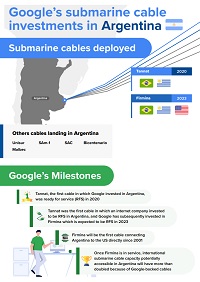
Google is an important stakeholder in the international Internet ecosystem, handling rapidly growing traffic for its users and cloud customers. To manage these growing capacity requirements, Google invests in submarine cable infrastructure, both in LAC and at a global level. So far in LAC, Google has spearheaded the launch of three international submarine cables: Monet (linking Brazil and the US), Tannat (connecting Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil) and Curie (connecting Chile, Panama, and the US). It has also led the deployment of a domestic cable in Brazil, Junior, which connects the states of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. In 2021 it announced a fifth system, Firmina, due to be ready for service in 2023, and will link the eastern US to Brazil, Uruguay, and Argentina. Google has also invested in other infrastructure, to which the cables provide increased connectivity, including its data center in Santiago (Chile), as well as cloud regions in São Paulo (Brazil) and Santiago (Chile). Plans for a third cloud region in LAC, in Mexico, were announced in July 2022.
Increased levels of connectivity in a region bring a wide range of benefits, both to businesses and to society as a whole. Benefits from submarine and terrestrial fiber projects include a reduction in latency and Internet Protocol (IP) transit prices, as well as increased bandwidth per Internet user. These benefits have led to an increase in the number of Internet users in the region, and an increase in data consumption.
As such, Google’s submarine cable infrastructure investments are contributing to better, lower-cost connectivity in LAC. The positive impacts on Internet penetration and data usage are estimated to enhance economic growth in terms of both gross domestic product (GDP) and job creation. We estimate that Google’s submarine cable deployments in the region will lead to a cumulative increase in GDP of USD178 billion between 2017 and 2027 (value in real 2021 USD), compared to a ‘counterfactual’ scenario in which these cables would not have been deployed. This represents an annual GDP increase of 1.08% in 2027 in the five countries in which Google’s cables land. The economic uplift is estimated to support the creation of around 740 000 additional jobs by 2027.
The regulatory and policy environment for submarine cable deployment is not always clearly defined or easily accessible in LAC countries, though there are differences between the various markets. With a transparent, consistent licensing regime, the foreign investments that appear to be generally welcomed in LAC should continue to be made, allowing businesses and end users in the region to benefit from better connectivity systems.
We collaborated on this report with Prof. Neil Gandal from Tel Aviv University.
Infographics:

David Abecassis
Partner, expert in strategy, regulation and policy
Tom Wicken
Consultant
Andrea Betteto
Consultant