Operators have an incentive to enter the SME cyber-security market and are developing effective strategies
The market for cyber-security solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years and telecoms operators will capture a growing share of revenue in that market. Our recent report, Approaches to cyber security for SMEs: ten operator case studies, assesses what operators are doing to sell cyber-security services to SMEs.
There are several strategies that we think are likely to be effective for operators when trying to sell cyber-security services to SMEs: bundling services with connectivity, leveraging expertise in the enterprise market, investing in offering training and advice for SMEs, and developing a broader portfolio of mobile security solutions.
Operators have a strong incentive to enter the cyber-security market, but offering these services is not straightforward
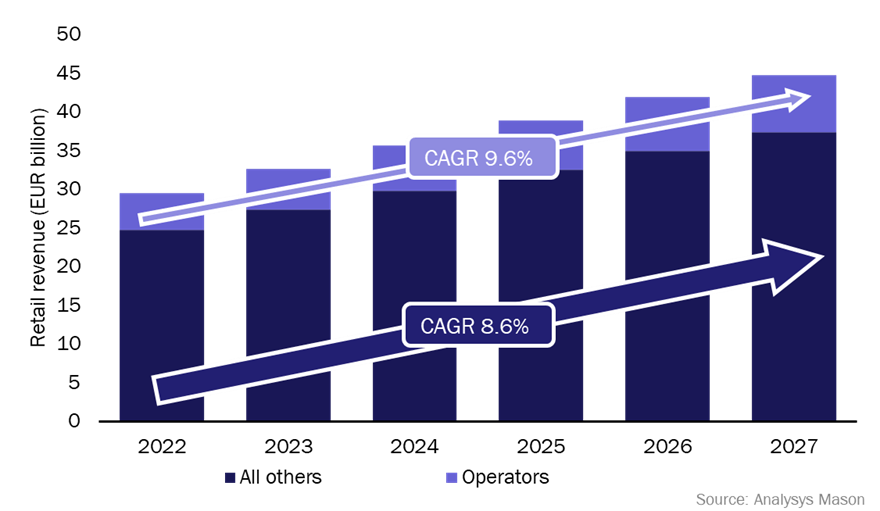
IT services will account for over 60% of incremental revenue that operators will generate from SMEs between 2022 and 2027. The public cloud services segment of the IT services market will be the largest and fastest growing in terms of revenue between 2022 and 2027. Operators will typically account for a small share of the overall market (~6% of revenue), but will account for a significant share of revenue in the SME cyber-security market (17%). Operator revenue from SME cyber-security services will grow at a CAGR of 9.6% between 2022 and 2027 (Figure 1), outperforming other cyber-security providers in the market.
Figure 1: Operators and other providers’ cyber-security revenue from SMEs, worldwide, 2022–20271
Offering IT services can be difficult for operators; many of the services lie outside their traditional expertise of connectivity and they are competing with IT specialists in a crowded market. However, the benefits of offering these services, such as incremental revenue, improved differentiation and reduced churn, outweigh these difficulties. The cyber-security market has some unique characteristics for operators. Network security and some mobile security solutions are closer to operators’ core competencies than other solutions such as offering IaaS/PaaS solutions, giving operators a logical starting point to enter the market.
However, offering cyber-security services is not straightforward. Many operators noted it is more difficult to engage with SMEs to adopt cyber-security solutions compared to other IT services. Some operators reported that SMEs are easier to work with if they have already experienced a cyber-security incident. Additionally, the cyber-security market is crowded; many cyber-security specialists are serving the market, with vendors selling directly to the enterprise market and managed service providers (MSPs) active in supplying security to SMEs. Orange has shown it is possible for an operator to become a leading cyber-security provider, although significant time and capital investments are required.
Operators’ approaches to offering cyber-security solutions for SMEs share common themes
Our case studies report evaluates each operator’s offering in three main categories.
- Fixed cyber-security services that protect a fixed network or sit on devices that are primarily connected to their network such as desktops or servers.
- Mobile cyber-security services that protect business mobile devices.
- Cyber-security training: programmes that are offered by operators to increase SME’s awareness of the need for cyber-security services.
The report also groups the operators according to three categories; pan-regional operators, large incumbent operators and domestic operators. The pan-regional operators included often have dedicated IT or cyber-security divisions, hence more resources to invest in this area. Despite this, the approaches of the operators share some similarities (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Overview of the typical relative breadth for each cyber-security category, by operator type
| Operator type | Mobile | Fixed | Training |
| Pan-regional | All | All | All |
| Large incumbent | Most | All | All |
| Domestic | Often limited | All | Often limited |
Source: Analysys Mason
Generally, the pan-regional operators have the most complete offerings relative to the other operator types. They have invested significant resources in their enterprise security offerings and are applying this expertise to the SME market. Regardless of these differences, common themes between all approaches emerged.
Operators should expand their mobile cyber-security offerings and become trusted security advisors to SMEs
Operators are taking common approaches to selling cyber-security services to SMEs and these approaches are likely to apply to most operators.
- Bundling cyber-security services with connectivity services is the most common differentiator that operators cited for their cyber-security solutions. Doing this offers SMEs price savings compared to buying the solutions separately, with some operators also providing management of all solutions from one platform as a further differentiator. BT, KPN and Telefónica are taking this approach further and bundling some basic cyber-security services with some, or all, of their business broadband packages for no extra charge. This helps operators to justify their prices and reduce churn to alternative connectivity providers.
- Operators with well-established security division can use this expertise to support standardised offers for SMEs. A good example of this is Telefónica’s cyber-security bundles being fully managed by its range of security operations centres (‘SoCs’), which were initially created for enterprise customers. These offerings are typically aimed at SMEs that have advanced cyber-security needs.
- Operators without established security brands will have to invest time in becoming trusted advisers to SMEs. These operators should invest time in offering impartial cyber-security advice to SMEs to help gain their trust and offer a range of cyber-security training and assessments to these SMEs. They should initially offer relatively simple solutions that are packaged with connectivity services, as discussed before.
- Investment in mobile security portfolios. The mobile cyber-security portfolios of most operators are relatively narrow when compared to their fixed offerings, despite there being the same advantages to offering mobile cyber-security as they do for fixed. The mobile cyber-security space tends to be simpler than the fixed market and could, therefore, offer smaller operators a chance to play a large part. For more information about operator strategies in this market, see Analysys Mason’s Approaches to cyber security for SMEs: ten operator case studies.
For more information, see Analysys Mason’s Operator business services for SMEs: worldwide forecast 2022–2027.
Article (PDF)
DownloadAuthor


